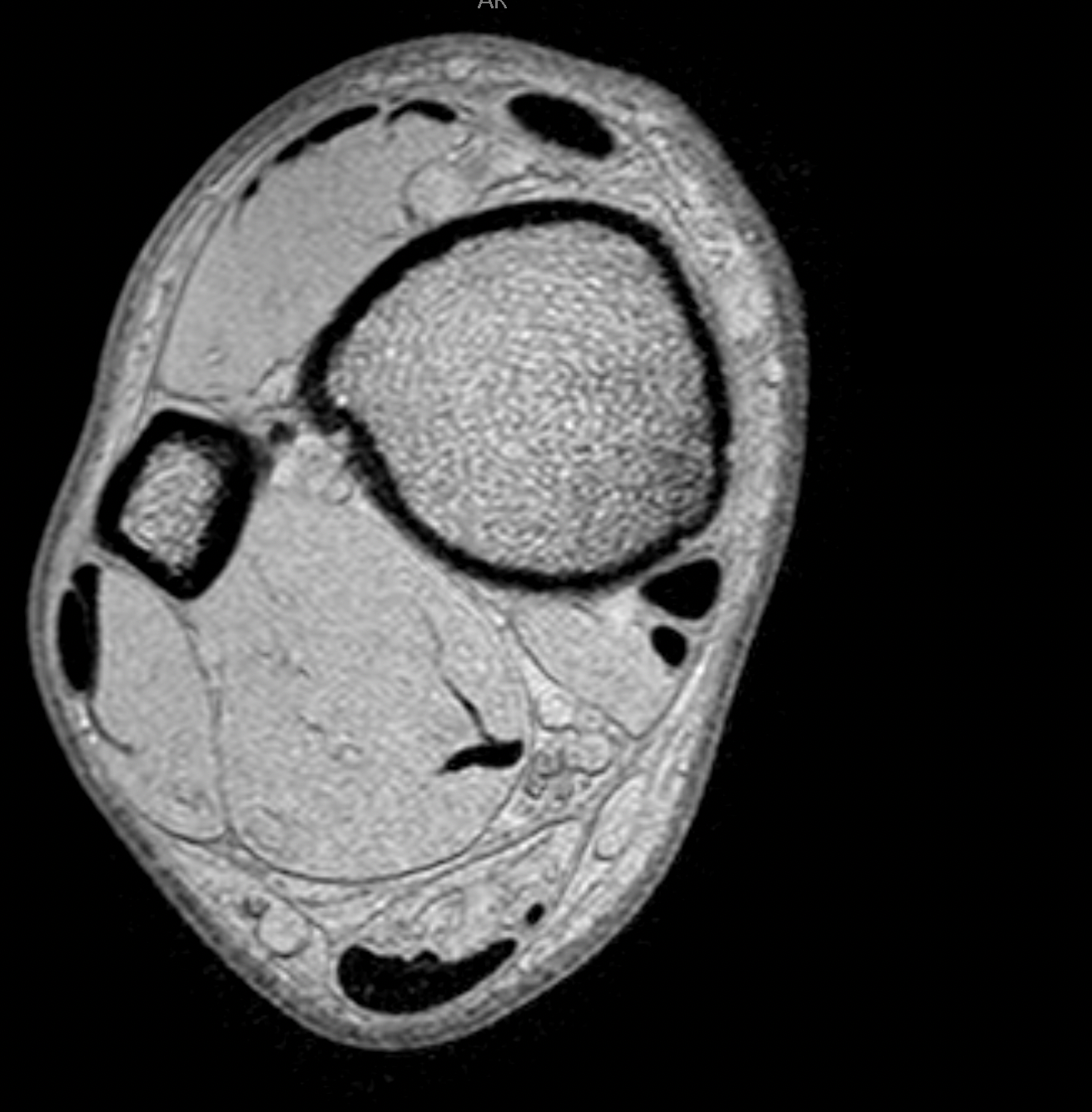
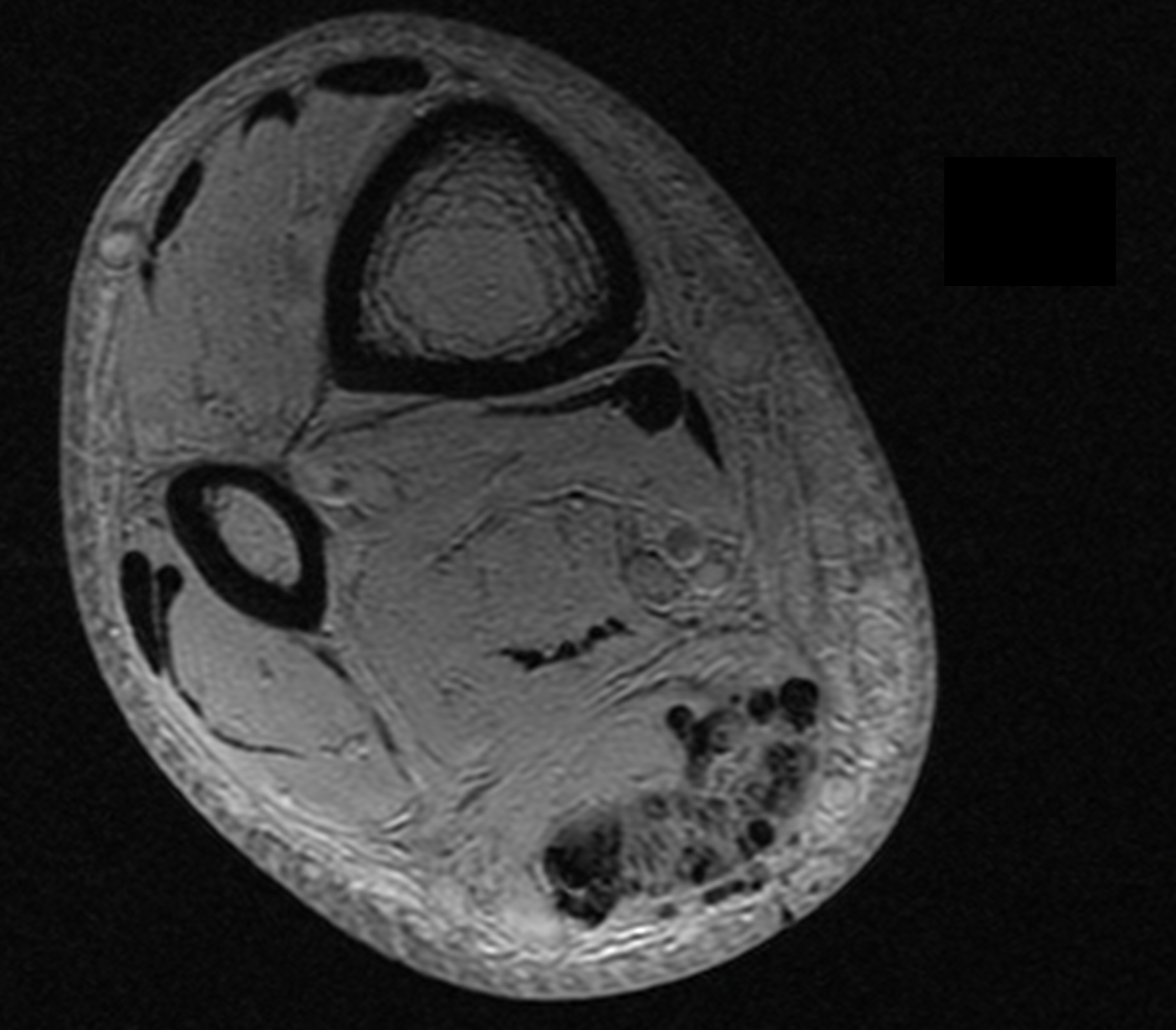
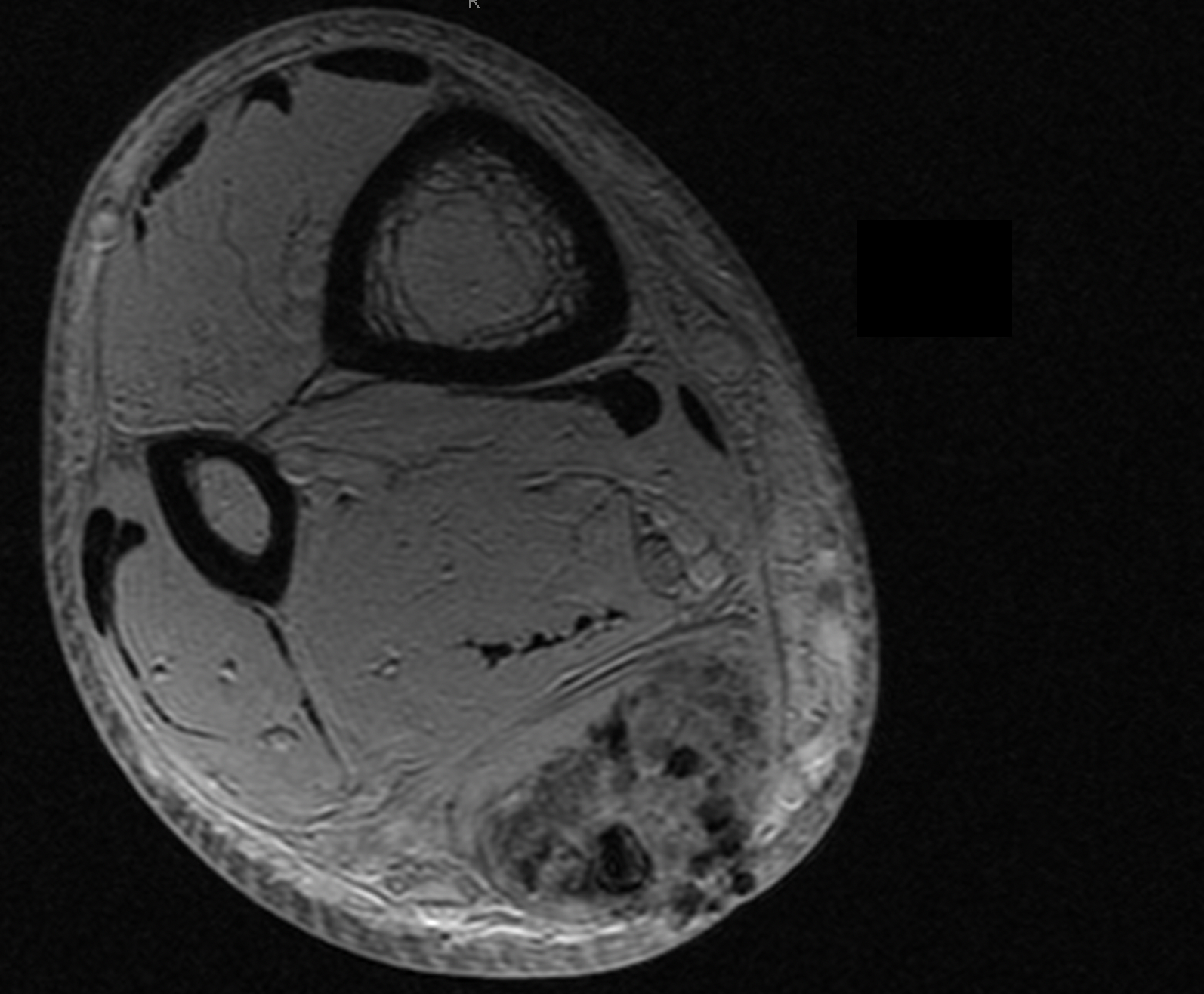
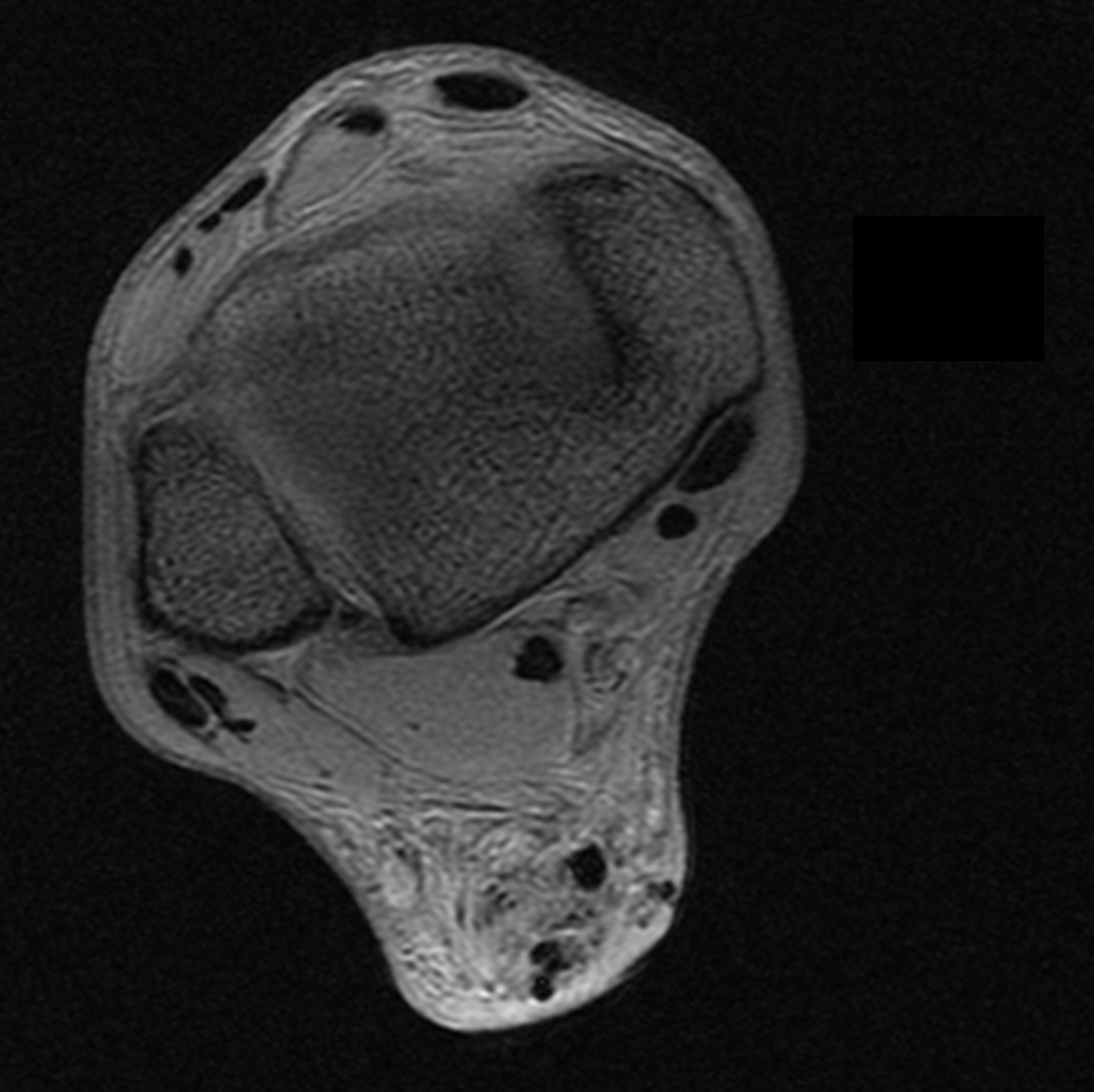
Tendon injuries are very often associated with fluid accumulation in the surrounding tissues. Edema within adjacent tissues may also occur in cases of ongoing inflammation such as in Achilles tendon bursitis.
This parameter assesses the presence of edema in the interfacial compartment of the tendon and the surrounding tissues. It should not be mistaken with the lower limb edema and its increase of circumference.
In radiological assessment, the presence of edema in the surrounding tissues is indicated by blurring of fat pad structures and increased MR signal intensity in T2 and STIR sequences. A highly intense signal in the surrounding tissues suggests a higher degree of edema.